Which Chart Type Displays The Data Vertically?
Top 16 Types of Chart in Data Visualization
Look at the following dashboard, practice you know how many types of chart are there?

In the era of information explosion, more than and more data piles upwards. Nevertheless, these dense data are unfocused and less readable. And then we need information visualization to help data to be hands understood and accepted. By contrast, visualization is more intuitive and meaningful, and it is very important to use advisable charts to visualize data.
In this mail, I will introduce the height 16 types of chart in data visualization, and clarify their application scenarios to help y'all quickly select the blazon of chart that shows the characteristics of your data.
Annotation: All the charts in the article are taken from the data visualization tool FineReport, and the personal download is completely complimentary.
i. Column Chart
Cavalcade charts use vertical columns to show numerical comparisons between categories, and the number of columns should not be also large (the labels of the axis may announced incomplete if there are too many columns).

The column chart takes advantage of the height of the column to reflect the difference in the information, and the human center is sensitive to height differences. The limitation is that information technology is simply suitable for small and medium-sized data sets.

Application Scenario: comparison of classified data
2. Bar Chart
Bar charts are similar to column charts, merely the number of bars can be relatively large. Compared with the column chart, the positions of its two axes are changed.


Application Scenario: comparison of data (the category name tin can be longer because at that place is more space on the Y axis)
3. Line Nautical chart
A line chart is used to show the change of data over a continuous time interval or time span. It is characterized past a trend to reflect things as they change over time or ordered categories.
It should be noted that the number of data records of the line graph should be greater than ii, which can be used for trend comparison of big data volume. And it is better not to exceed five polylines on the aforementioned graph.

Awarding Scenario: tendency of data volume over time, comparison of series trends
4. Area Nautical chart
The expanse chart is formed on the footing of the line chart. It fills the area betwixt the polyline and the axis in the line chart with color. The filling of the color can better highlight the trend information.
The fill color of the area nautical chart should have a certain transparency. The transparency can assistance the user to discover the overlapping relationship between different series. The area without transparency will cause the different series to cover each other.


Application Scenario: series ratio, time tendency ratio
5. Pie Chart
Pie charts are widely used in diverse fields to represent the proportion of dissimilar classifications, and to compare diverse classifications by the arc.
The pie chart is not suitable for multiple series of data, because as the series increase, each piece becomes smaller, and finally the size distinction is non obvious.

A pie chart can likewise exist made into a multi-layer pie chart, showing the proportion of different categorical data, while also reflecting the hierarchical relationship.

Application Scenario: series ratio, series size comparing (rose diagram)
six. Scatter Plot
The besprinkle plot shows 2 variables in the course of points on a rectangular coordinate system. The position of the signal is determined past the value of the variable. Past observing the distribution of the data points, nosotros can infer the correlation between the variables.
Making a besprinkle plot requires a lot of information, otherwise the correlation is not obvious.


Awarding Scenario: correlation assay, data distribution
7. Bubble Chart
A bubble chart is a multivariatechart that is a variant of a scatter plot. Except for the values of the variables represented past the X and Y axes, the area of each bubble represents the tertiary value.
Nosotros should note that the size of the chimera is express, and too many bubbling will brand the chart difficult to read.
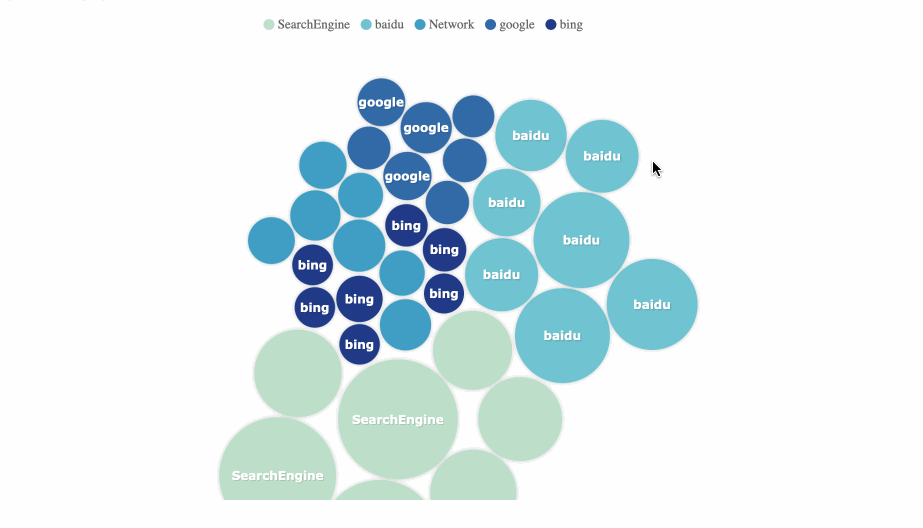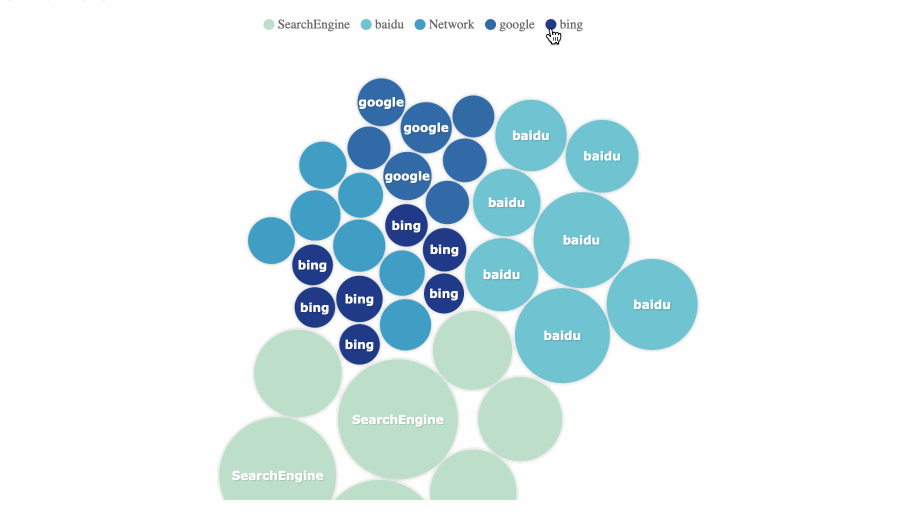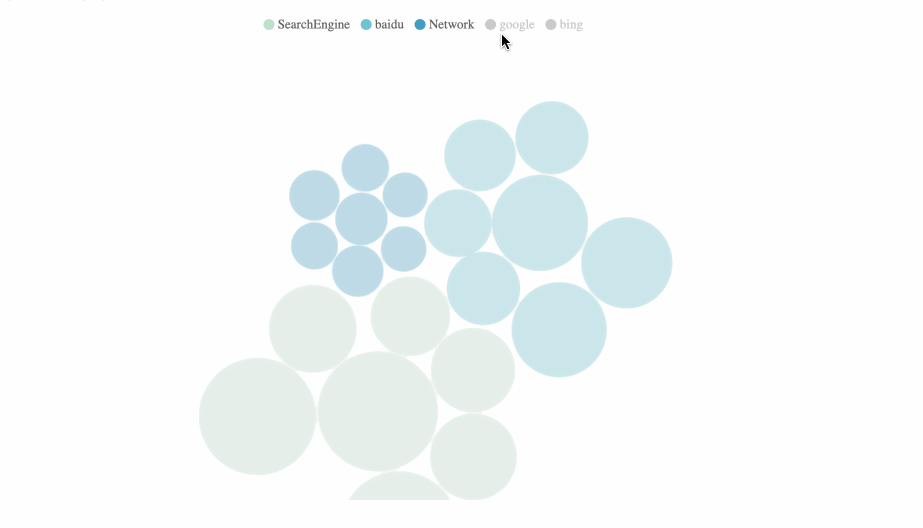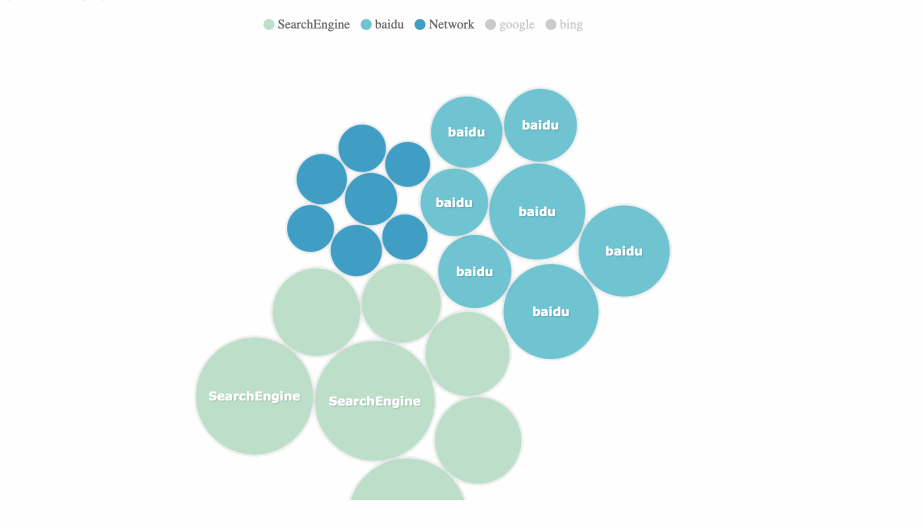
Application Scenario: comparing of classified data, correlation assay
8. Gauge
A gauge in information visualization is a kind of materialized chart. The scale represents the metric, the pointer represents the dimension, and the pointer angle represents the value. It can visually represent the progress or actual situation of an indicator.
The gauge is suitable for comparison between intervals.

Information technology tin also exist made into a ring or a tube type, indicating the ratio.

Application Scenario: clock, ratio brandish
9. Radar Chart
Radar charts are used to compare multiple quantized variables, such equally seeing which variables have similar values, or if there are farthermost values. They also help to observe which variables in the data set take college or lower values. Radar charts are suitable for demonstrating job functioning.

The radar nautical chart also has a stacked column mode that tin can be used for ii-way comparing betwixt classification and serial, while as well representing the proportion.

Awarding Scenario: dimension analysis, series comparison, series weight analysis
10. Frame Diagram
The frame diagram is a visual ways of presenting the hierarchy in the course of a tree construction, which clearly shows the hierarchical relationship.

Application Scenario: bureaucracy display, process display
11. Rectangular Tree Diagram
The rectangular tree diagramis suitable for presenting data with hierarchical relationships, which can visually reverberate the comparing between the same levels. Compared with the traditional tree structure diagram, the rectangular tree diagram makes more than efficient use of space and has the function of showing the proportion.
Rectangular tree diagrams are suitable for showing the hierarchy with weight relationships. If it is not necessary to reflect the proportion, the frame diagram may be clearer.

Application Scenario: weighted tree data, proportion of tree data
12. Funnel Chart
The funnel chart shows the proportion of each phase and visually reflects the size of each module. It'south suitable for comparing rankings.

At the same time, the funnel chart can too be used for comparison. We arrange multiple funnel charts horizontally and the information contrast is likewise very clear.

Awarding Scenario: data ranking, ratio, standard value comparison
13. Discussion Deject Chart
The word cloud is a visual representation of text data. Information technology is a deject-like color graphic composed of vocabulary. It is used to display a large amount of text data and can quickly help users to perceive the nearly prominent text.
The word cloud nautical chart requires a large amount of data, and the caste of bigotry of the data is relatively large, otherwise the effect is not obvious. And information technology is not suitable for accurate analysis.

Application Scenario: keyword search
14. Gantt Nautical chart
The Gantt nautical chart visually shows the timing of the mission, the actual progress and the comparison with the requirements. Then managers can hands sympathise the progress of a task (project).

Awarding Scenario: project progress, state changes over time, project process
15. Map
The map is divided into three types: regional map, point map, and menstruum map.
(1) Regional Map
A regional map is a map that uses color to stand for the distribution of a certain range of values on a map sectionalization.

Application Scenario: comparison and distribution of data
(two) Indicate Map
A betoken map is a method of representing the geographical distribution of data by plotting points of the aforementioned size on a geographical background.
The distribution of points makes information technology easy to grasp the overall distribution of data, only it is not suitable when you need to observe a single specific data.

Application Scenario: distribution of data
But if you replace the point with the bubble, then the signal map tin not only show the distribution but also roughlycompare the size of the information in each region.

(three) Flow Map
The flow map displays the interaction data between the outflow area and the inflow surface area. Information technology is normally expressed by the line connecting the geometric centers of gravity of the spatial elements. The width or color of the line indicates the menstruation value.
Flow maps aid to illustrate the distribution of geographic migration, and the use of dynamic flow lines reduces visual clutter.

Application Scenario: flow, distribution and comparison of data
16. Heatmap
The heatmap is used to indicate the weight of each point in the geographic area. In add-on to the map as the groundwork layer, yous can also utilise other images. And Color in a heatmap usually refers to density.

Awarding Scenario: regional visits, rut distribution, distribution of various things
At Concluding
All of the above are the sixteen frequently used types of chart in data visualization. If yous want to get started with information visualization, I suggest y'all kickoff by learning to brand these bones charts and practise with an easy-to-employ tool like FineReport.
Some people may think that the basic charts are likewise simple and primitive, and they tend to utilise more complicated charts. All the same, the simpler the nautical chart, the easier information technology is to assist people quickly understand the data. Isn't that the about important purpose of data visualization? And so please don't underestimate these basic charts. Because users are most familiar with them. They should exist considered for priority as long every bit they are applicable.
You might too be interested in…
How Can Beginners Pattern Cool Data Visualizations?
A Beginner's Guide to Business concern Dashboards
4 Uses of Data Maps in Business Analysis
Which Chart Type Displays The Data Vertically?,
Source: https://towardsdatascience.com/top-16-types-of-chart-in-data-visualization-196a76b54b62
Posted by: dupreysomighten.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Which Chart Type Displays The Data Vertically?"
Post a Comment